METHODS OF CALCULATION OF REDUCE LEVEL
The following are two systems of calculating reduce level:
[1]. The collimation systems or height of
instrument system (HI)
[2]. The rise and fall system.
[1]. The collimation systems or height of instrument system (HI).
The reduce level of the line of collimations
is said to be the height of instrument. In this system, the height of line of
collimation is found out by adding the backsight reading to the RL of the BM on
which of the BS is taken. Then the RL of the intermediate points and the change
points are obtained by subtracting the respective staff readings from the
height of the instrument (HI).
The level is then shifted for the next set
up and again height of the line of collimation is obtained by adding the
backsight reading to the RL of the change point (which was calculated in the
first set up).
So, the height the height of instrument is
different in different set up of the level. Two adjacent planes of collimation
correlated at the change point by an FS reading from one setting and a BS
reading from the next setting.
It should be remembered that, in this system, the RLs of unknown points are to be found out by deducting the staff readings from the RL of the height of the instrument.
Consider Fig.-L.24
[a]. RL
of HI in first setting = 100.00 + 1.150 = 101.150
RL
of A = 101.150 – 1.355 = 99.795
RL of B = 101.150 – 2.45 = 98.700
[b]. RL
of HI in second setting = 98.700 + 1.875 = 100.575
RL of C = 100.575 – 0.890 = 99.685
RL of D = 100.575 – 1.655 = 98.920 and so on,
Arithmetical
check: ΣBS – ΣFS = Last RL – 1st RL
The difference between the sum of backsight
and that of foresight must be equal to the difference between the last RL and
the first RL. This check verifies the calculation of the RL of the HI and that
of the change point. There is no check on RLs of the intermediate points.
[2]. The rise-and-fall system.
In this system, the difference of level
between two consecutive points is determined by comparing each forward staff
reading with the staff reading at the immediately preceding point.
If the forward staff reading is smaller than
the immediately preceding staff reading, a rise is said to have occurred. The
rise is added to the RL of the preceding point to get the RL of forward point.
If the forward staff reading is greater than the immediately preceding staff reading, its means there has been a fall. The fall is subtracted from the RL of the preceding point to get the RL of forward point.
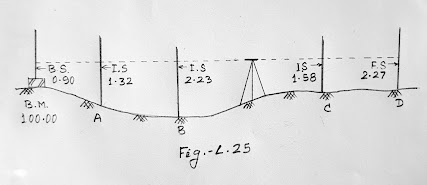
Consider
Fig.-L.25
Point A
(with respect to BM) = 0.90 – 1.32 = -0.42 (fall)
Point B
(with respect to A) = 1.32 – 2.23 = -0.91 (fall)
Point C
(with respect to B) = 2.23 – 1.58 = +0.65 (rise)
Point D
(with respect to C) = 1.58 – 2.27 = -0.69 (fall)
RL of
BM = 100.00
RL of A
= 100.00 – 0.42 = 99.58
RL of B
= 99.58 – 0.91 = 98.67
RL of C
= 98.67 + 0.65 = 99.32
RL of D = 99.32 - 0.69 = 98.63
Arithmetical check: ΣBS – ΣFS = Σrise - Σfall = Last RL – 1st RL
In this method, the difference between the
sum of BSs and that of FSs the difference between the sum of rises and that of
falls and the difference between the last RL and first RL must be equal.
Example The following
consecutive readings were taken with an automatic level along a chain line with
a common interval of 15 metre. The first reading was at a chainage of 180 metre
where the RL is 103.345. The instrument was shifted after the fifth and eleventh
readings.
2.450, 3.775, 1.605, 0.875, 0.790, 1.670, 1.485, 2.065, 1.385, 1.570, 1.295, 1.440, 2.495, 1.370, 0.945 and 1.070
|
1. By collimation System: |
|||||||
|
Station Point |
Chainage (in Metre) |
BS |
IS |
FS |
RL of collimation line (HI) |
Reduce Level (RL) |
Remarks |
|
1 |
180.00 |
2.450 |
|
|
105.795 |
103.345 |
|
|
2 |
195.00 |
|
3.775 |
|
105.795 |
102.020 |
|
|
3 |
210.00 |
|
1.605 |
|
105.795 |
104.190 |
|
|
4 |
225.00 |
|
0.875 |
|
105.795 |
104.920 |
|
|
5 |
240.00 |
1.670 |
|
0.790 |
106.675 |
105.005 |
Change Point (CP) |
|
6 |
255.00 |
|
1.485 |
|
106.675 |
105.190 |
|
|
7 |
270.00 |
|
2.065 |
|
106.675 |
104.610 |
|
|
8 |
285.00 |
|
1.385 |
|
106.675 |
105.290 |
|
|
9 |
300.00 |
|
1.570 |
|
106.675 |
105.105 |
|
|
10 |
315.00 |
1.440 |
|
1.295 |
106.820 |
105.380 |
Change Point (CP) |
|
11 |
330.00 |
|
2.495 |
|
106.820 |
104.325 |
|
|
12 |
345.00 |
|
1.370 |
|
106.820 |
105.450 |
|
|
13 |
360.00 |
|
0.945 |
|
106.820 |
105.875 |
|
|
14 |
375.00 |
|
|
1.070 |
106.820 |
105.750 |
|
|
Total
= |
5.560 |
3.155 |
|||||
Arithmetical Check: | |||||||
ΣBS - ΣFS = 5.560 - 3.155 = + 2.405 Last RL - 1st RL = 105.750 - 103.345 = + 2.405 | |||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arithmetical Check:
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Next post
on “DIFFICULTIES FACED IN LEVELLING”)




No comments:
Post a Comment